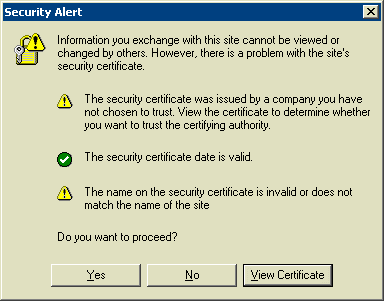
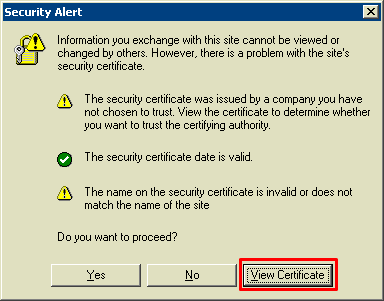
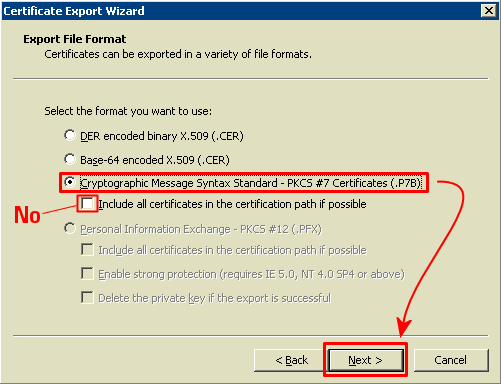
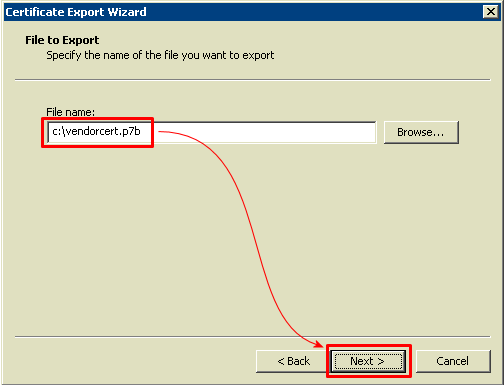
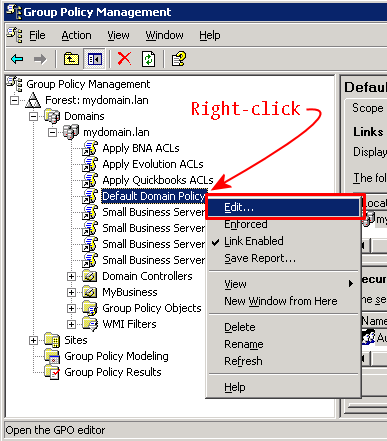
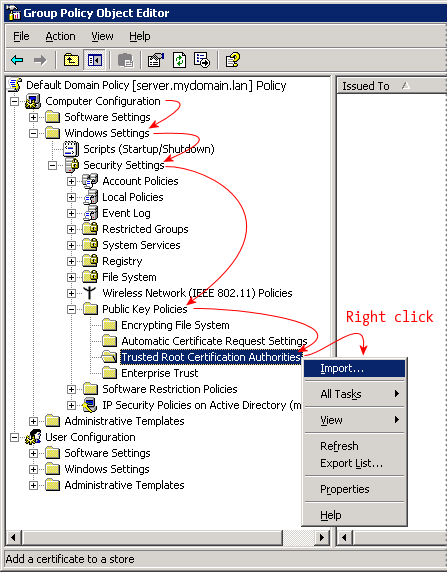
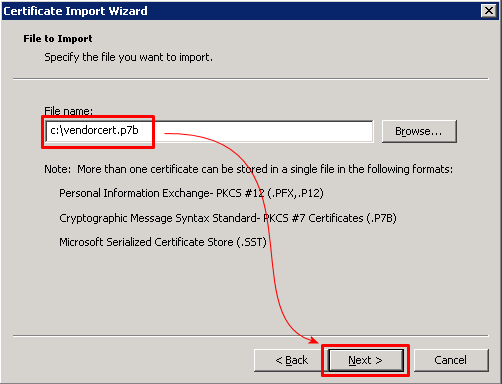
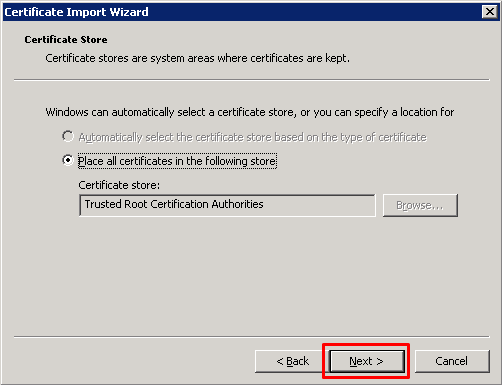
1. get system performance status
- 현재 CPU & Memory, Traffic 사용량, Session수 및 Uptime 확인
2. get system status
- OS Version 및 Serial 정보 확인
3. diag debug crashlog read
- 프로세서 Crash 내역 및 FortiGate의 주요 이슈 사항 확인
4. diag log alertconsole list
- 관리자 계정 Login 실패 기록, 장비 재시작, 전원 off, FortiGuard 업데이트 내역 확인
5. diag hardware device nic port1
- 해당 Port의 Speed/Duplex 및 Error확인 가능
6. diag netlink device list
- 전체 Port에 대한 Error 확인
7. get route info routing-table all
- Routing Table 확인
8. get sys arp
- ARP Table 확인
9. get system interface
- Interface IP정보 확인
10. 기타
# excute tac report
# fnsysctl ls -l /dev/shm
# fnsysctl ls -l /tmp
# diagnose hardware sysinfo shm
# diagnose hardware sysinfo slab
# diagnose hardware sysinfo interrupt
# diagnose ip arp list
# diagnose ip rtcache list
# diagnose ip router command show show int
# diagnose ips anomaly list
# diagnose ips anomaly status
# diagnose ips dissector status
# diagnose ips packet status
# diagnose ips raw status
# get ips session
# diagnose sys session stat
# get system auto-update status
# get system auto-update versions
# diagnose test update info
# diagnose sys flash list
# fnsysctl df -k
# diagnose sys logdisk smart
# diagnose sys logdisk status
# diagnose sys ha status
# diagnose sys ha showcsum
# diagnose sys ha hadiff status
# diagnose sys ha dump-by all-vcluster
# diagnose sys ha dump-by rcache
# diagnose sys ha dump-by all-group
# diagnose sys ha dump-by memory
# diagnose sys ha dump-by vdom
# diagnose sys ha dump-by debug-zone
# diagnose sys ha dump-by kernel
# diagnose sys ha dump-by device
# get sys session-info statistics
# get system session-info ttl
# get system session-helper-info list
# diagnose netlink aggregate list
# diagnose netlink brctl list
# diagnose netlink device list
# diagnose firewall fqdn list
# diagnose firewall iplist list
# diagnose firewall ipmac list
# diagnose firewall ipmac status
# diagnose firewall iprope list
# get firewall proute
# diagnose firewall schedule list
# get system performance firewall statistics
# get router info routing-table all
# get router info routing-table database
# get vpn ipsec stats crypto
# get vpn ipsec tunnel details
# get vpn status ssl list
# get webfilter ftgd-statistics
# get webfilter status
# diagnose spamfilter fortishield statistics list
# diagnose spamfilter fortishield servers
# get hardware nic mgmt2
# get hardware nic mgmt1
# get hardware nic port32
# get test proxyacceptor 1
# get test proxyacceptor 4
# get test proxyworker 1
# get test proxyworker 4
# get test proxyworker 4444
# get test http 444
# get test http 11
# diagnose sys scanunit stats all
# get test urlfilter 10
# diagnose sys sip-proxy filter clear
# diagnose sys sip-proxy redirect list
# diagnose sys sip-proxy config list
# diagnose sys sip-proxy config profiles
# diagnose sys sip-proxy meters list
# diagnose sys sip-proxy stats proto
# diagnose sys sip-proxy stats call
# diagnose sys sip-proxy stats udp
# diagnose sys sip-proxy calls idle
# diagnose sys sip-proxy session list
# diagnose sys sccp-proxy stats list
# diagnose sys sccp-proxy phone list
# get test ipsmonitor 1
# get test ipsmonitor 3
# get test radiusd 5
# diagnose test application miglogd 6
# diagnose debug crashlog read